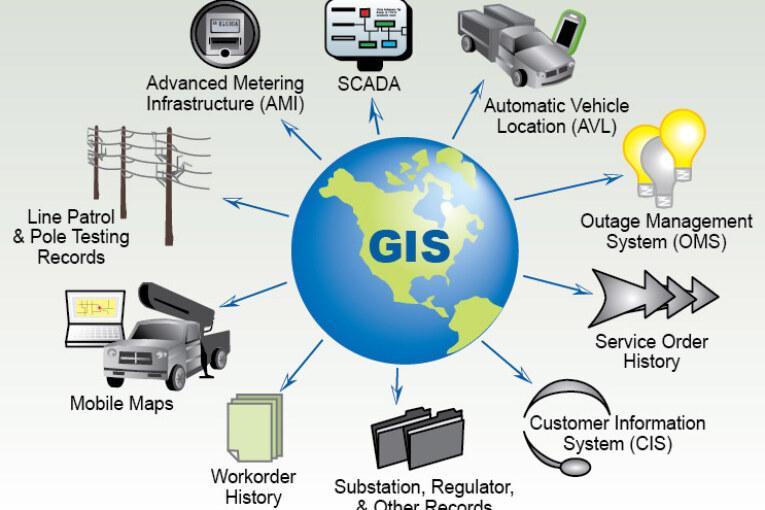
What is Geographic Information System?
Geographic Information System is a set of different tools in which we find integration and relationship of various components that help to carry out the following operations
- Reading, editing, and storing data
- Analysis of spatial data
- Obtaining results
A geographic information system is not only useful in the transportation business, to get road traffic data, but it’s also now part of our day-to-day activities, and in most cases, we do not realize it.
Most aspects of our lives have a spatial component, and more than 80% of the data we process daily is spatial data.
For example, the car route or the GPS of our car or your android and iPhone are spatial data, that is, they are geo-referenced.
How do Geographic Information Systems Work?
- To collect data
- To interpret and organize data
- To manage data
- To analyze data
- To present analysis or results
Data collection and Processing
Data with geographical, spatial, or temporal information can come from different sources.
For example, sensors, satellites, smartphones, video cameras, cameras, social networks,, or internet servers provide the raw data required for the geographic information systems.
Different methods can be used to collect data, depending on the data sources and the type of data available.
However, whichever the data source and type, it must be converted to digital information.
To capture data that is already available digitally, the data sources can be connected to the systems via various interfaces.
Once the data is read, it will be structured, prepared, and converted into the required file formats for further processing.
As part of the analysis, the geographical information system recognizes patterns or dependencies of the 1, 2, or multi-dimensional data.
This creates deeper insights into the geographical and spatial relationships.
The analysis of the results is in the form of static or interactive geographic models, maps, or animations and can now be presented to the target audience.
Data storage
The spatial data begins to be structured and organized within the GIS, based on the location, the relationship between them, and the design.
However, it requires a digital medium such as a laptop, hard drive, or any place where we can store large amounts of data.
Final product
The last step is the production of data, for which a large number of formats can be used, among which the maps, graphs, simple or complex tables where the final data are compared, the charts, or simply an extensive report stand out.
Advantages of Geographic information system
These are some of the advantages of GIS application.
With GIS, it is possible and easy to calculate, in a more or less simple way, and especially fast, the existing routes between two or more points.
Since the data collected is usually geo-centered, it is easy to get location data, information, or happenings about a specific area.
Thanks to a series of guidelines that can be incorporated into the system, it is easy to find the relationships that may exist between one or more variables.
From the specific data of a specific area, and based on historical data, future models can be generated that allow us to know how much a specific area is expected to change.
Also, from historical data, it is possible to know how much an area has changed, in certain aspects, over the years, for example.
Conclusion
Due to the high volume of data that is collected and processed today, the applications of Geographic Information Systems are cut across different industries.
Also, with the advancement of technology in the field of applications has grown exponentially, and it is expected that they will continue to grow in the next years.